Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Ozone in the Food Industry: An Effective and Safe Solution
As the food industry continues to push for higher safety standards, sustainability, and operational efficiency, ozone stands out as a cutting-edge solution for sanitization. Approved by the FDA and USDA, ozone is a highly effective, eco-friendly disinfectant that is increasingly being adopted across all sectors of food production—from washing produce to sanitizing equipment and extending shelf life.
In this guide, we’ll explore what ozone is, how it works, and why it outperforms traditional sanitizers in modern food applications.
1. What Is Ozone and Why Is It So Effective?
Ozone (O₃) is a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms. It’s a powerful oxidizing agent—far more reactive than chlorine—and rapidly destroys bacteria, viruses, fungi, molds, and spores by breaking down their cell walls and disrupting metabolic processes.
Because it decomposes into oxygen after use, ozone does not leave behind toxic residues or by-products, making it ideal for food applications where clean label and chemical-free processing are key.
2. Mechanism of Action
Ozone’s antimicrobial activity is due to its ability to:
- Oxidize the lipid layers of cell membranes
- React with proteins and nucleic acids, damaging microbial DNA
- Break down organic matter and biofilms
This multi-targeted approach results in broad-spectrum microbial inactivation, including hard-to-kill pathogens like Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella spp., E. coli, Clostridium, and norovirus.
3. Key Applications of Ozone in the Food Industry
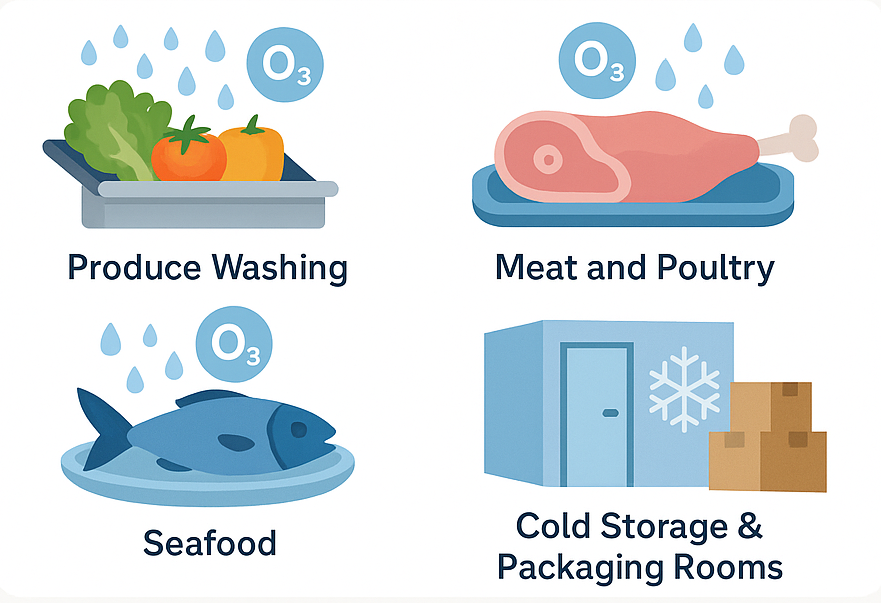
- Produce Washing: Ozone in water is widely used to reduce microbial load on fruits and vegetables, helping prevent spoilage and foodborne illness without altering taste, texture, or nutritional value.
- Meat and Poultry: Used to sanitize carcasses, processing surfaces, and chilling water, ozone helps reduce contamination by Salmonella and Listeria.
- Seafood: It helps eliminate surface bacteria and improve shelf life of fish, shrimp, oysters, and other seafood, while reducing odors.
- Dairy and Beverages: Ozone is applied in CIP systems to sanitize pipes, tanks, and filling equipment—eliminating the need for chemical-based cleaners.
- Grains, Cereals, and Spices: Used in gaseous form to reduce mold, insects, and mycotoxins in stored grains and spices.
- Cold Storage & Packaging Rooms: Ozone gas is introduced into cold rooms to control mold and bacteria on walls, crates, and even packaging materials.
4. Application Methods
- Ozonated Water: For direct contact with foods (fruits, vegetables, meat).
- Gaseous Ozone: For storage areas, air disinfection, or dry product sanitation.
5. Regulatory Approval and Safety
- FDA Approval (GRAS): Ozone is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for direct contact with food.
- USDA and EPA: Recognize ozone as an antimicrobial agent for food surfaces and processing environments.
6. Operational and Cost Benefits
- Reduces Chemical Use: Less need for chlorine, acids, or detergents.
- Water Savings: No rinse cycles required post-ozone treatment.
- Increased Shelf Life: Products stay fresher, longer.
- Worker Safety: Eliminates exposure to harsh chemicals.
- Sustainability: Lowers chemical waste and discharge.
7. Implementation Considerations
To implement ozone effectively, consider:
- Choosing the right ozone generator (output, gas or aqueous application)
- Proper dissolution: Use of Venturis or contact tanks for ozonated water
- Material compatibility: Stainless steel, Teflon, and ozone-resistant components are recommended
- Monitoring: Use ORP or ozone sensors to ensure safe and effective dosing
- Off-gas destruction: Use ozone destruct units to safely neutralize excess gas
Conclusion
Ozone is a game-changer in food safety and sanitation. Its powerful disinfection, absence of chemical residues, and environmentally friendly profile make it an ideal solution for modern food processors aiming to meet strict hygiene standards while lowering operational costs.
Whether you are washing produce, sanitizing equipment, or improving shelf life in storage, ozone delivers superior performance with minimal drawbacks.