KEY FEATURES:
- lower water and chemical consumption and time loss of the ozonation process than conventional wet processes.
- No need to store chemicals compared to the other conventional methods.
- No dangerous waste because of the decomposition of ozone into oxygen.
- No halogenated organic compounds (AOX) in wastewater.
Ozone For Textile: A New Trend in the Industry
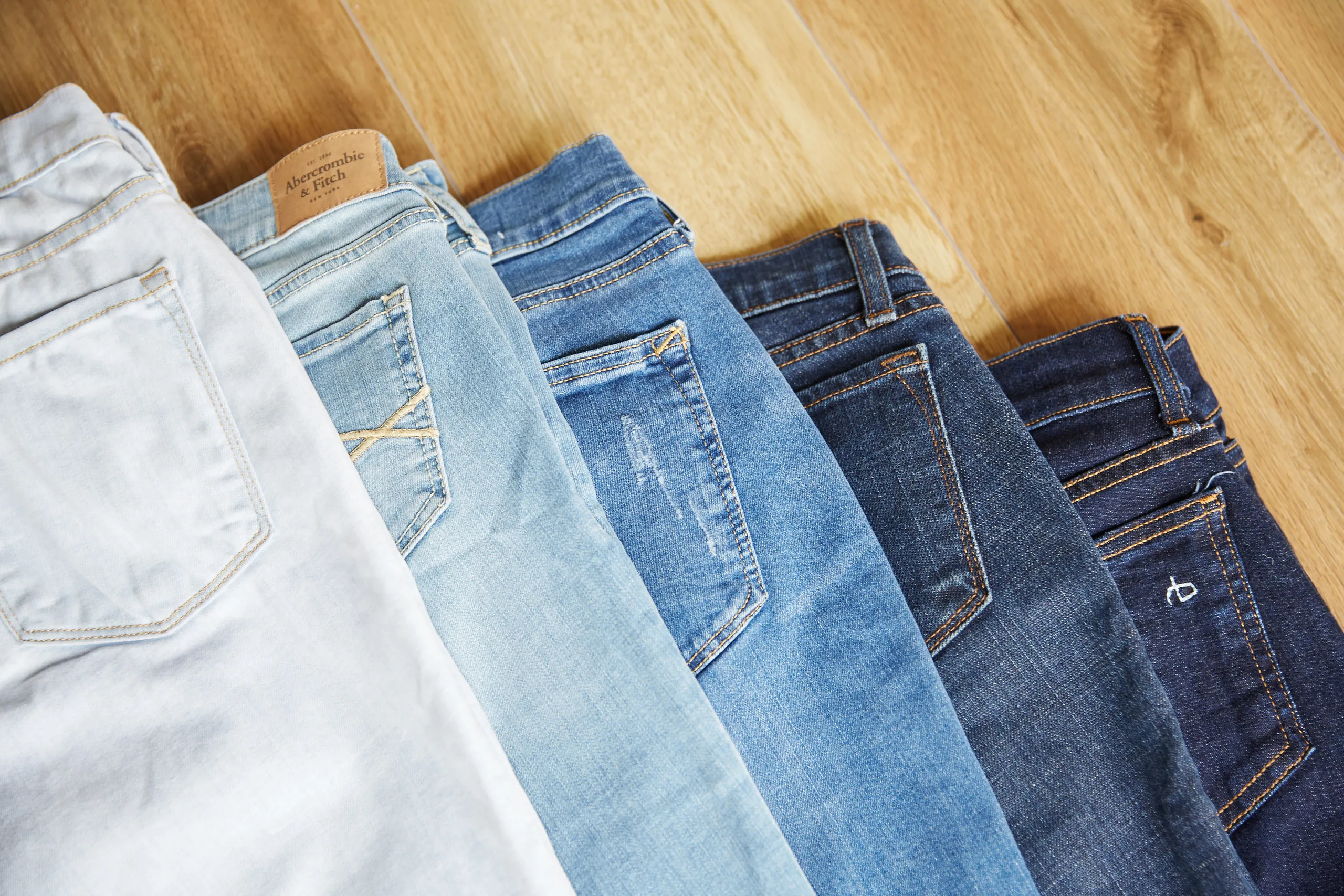
The textile industry relies on a variety of wet and dry processing methods—including pumice stone treatments, enzyme washes, bleaching, and mixed washing—to achieve specific fabric finishes. Among all sectors, textile dyeing and finishing are the most intensive in terms of water and energy consumption. For instance, the production of denim alone consumes approximately 350 million m³ of water annually. This high usage also leads to significant wastewater and solid waste generation. In response to environmental and economic concerns, ozone technology is emerging as a powerful, chemical-free, dry-bleaching alternative.
Ozonation: A Greener Textile Process
Ozonation is a dry, energy-efficient process that eliminates the need for water or steam. Its high oxidation potential enables the effective breakdown of dyes such as indigo, allowing for faster, cleaner fabric treatment. It can replicate the fading effects of traditional washing machines—without the water.
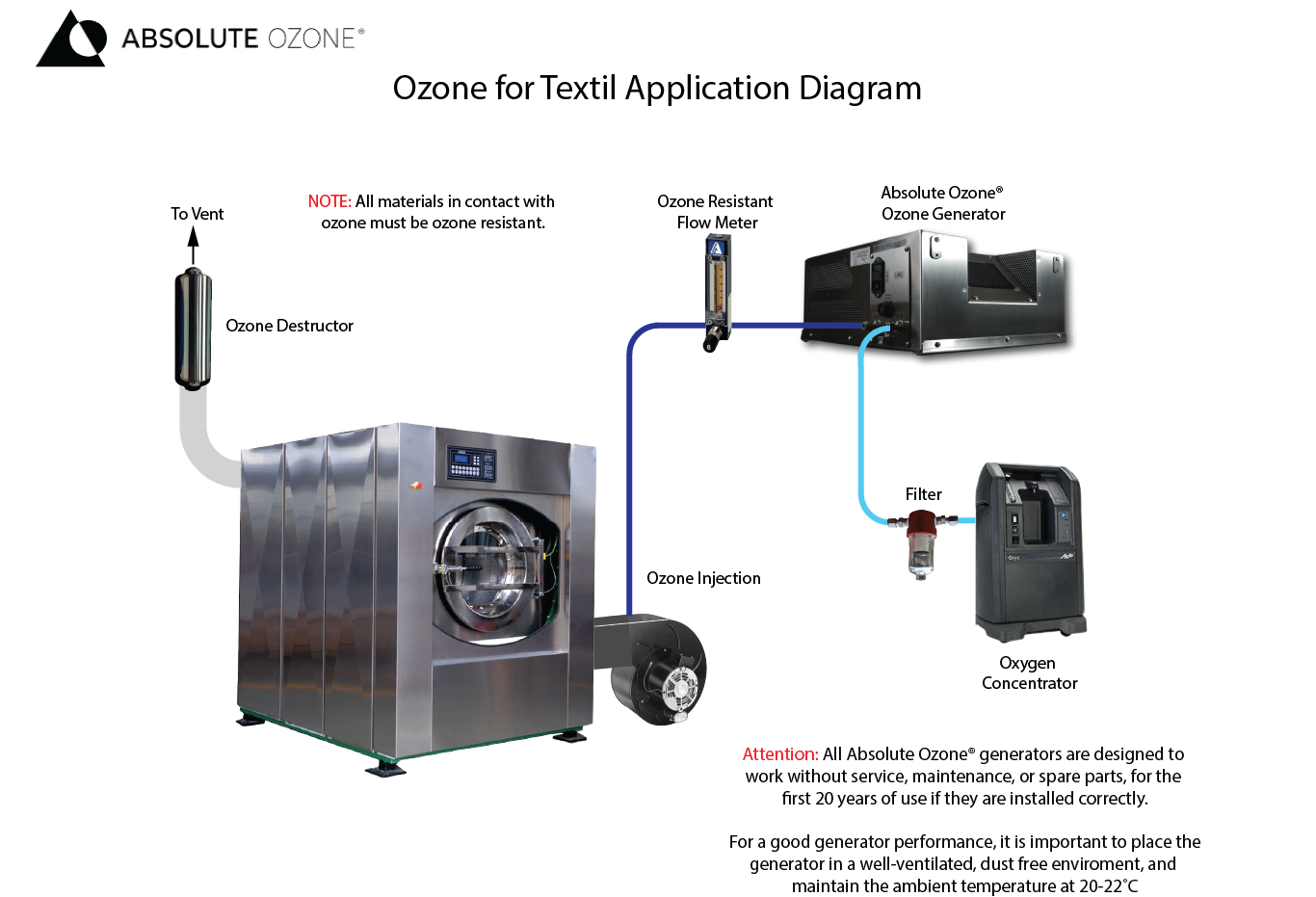
With Absolute Ozone® generators, industrial ozone treatment becomes a reliable, scalable solution. Our systems provide consistent and controlled bleaching performance, whether for denim or other textile materials.
Importantly, ozone decomposes naturally into oxygen, leaving no harmful residues. Unlike chlorine-based bleaching agents, ozone doesn't compromise fabric strength when properly applied—thanks to its short half-life and targeted decomposition of dyes rather than the textile fibers themselves.
Advantages of ozone laundry system in the textile industry
Ozone treatment proposed an economical solution to environmental pollution from textile processes.
- Environmental sustainability: Ozone drastically reduces the need for water and chemicals, supporting cleaner production and leaving zero toxic by-products.
- Energy efficiency: The process consumes less energy than traditional methods, contributing to lower utility costs and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Colour removal and oxidation: Ozone's oxidative power breaks down indigo and other dyes, achieving uniform fading and enhancing wash effects.
- Versatility: Ozone generation and dosage can be finely tuned to ensure consistent and repeatable results, enabling quality control at scale.
- Reduced water usage: By significantly cutting water consumption, ozone directly addresses one of the industry's biggest sustainability challenges.
Driving the Future of Sustainable Textiles
The global textile industry is increasingly adopting ozone technology for its economic and environmental benefits. It not only helps companies comply with international environmental regulations, but also enhances brand image by aligning with consumer demand for eco-friendly products. As sustainability becomes a key differentiator, ozone technology offers manufacturers a competitive edge, improved efficiency, and a powerful message of innovation.
Conclusion
Ozone represents a transformative approach in textile processing. It delivers:
- Lower water and energy use
- Minimal chemical dependency
- Cleaner waste management
- Sustainable development pathways
At Absolute Ozone®, we are proud to provide cutting-edge ozone generators that meet the evolving needs of the textile industry. By integrating ozone into your processes, you not only protect the environment—you also strengthen your brand, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the curve.