Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
How Do Ozone Generators Work: Understanding Ozone
What is Ozone?
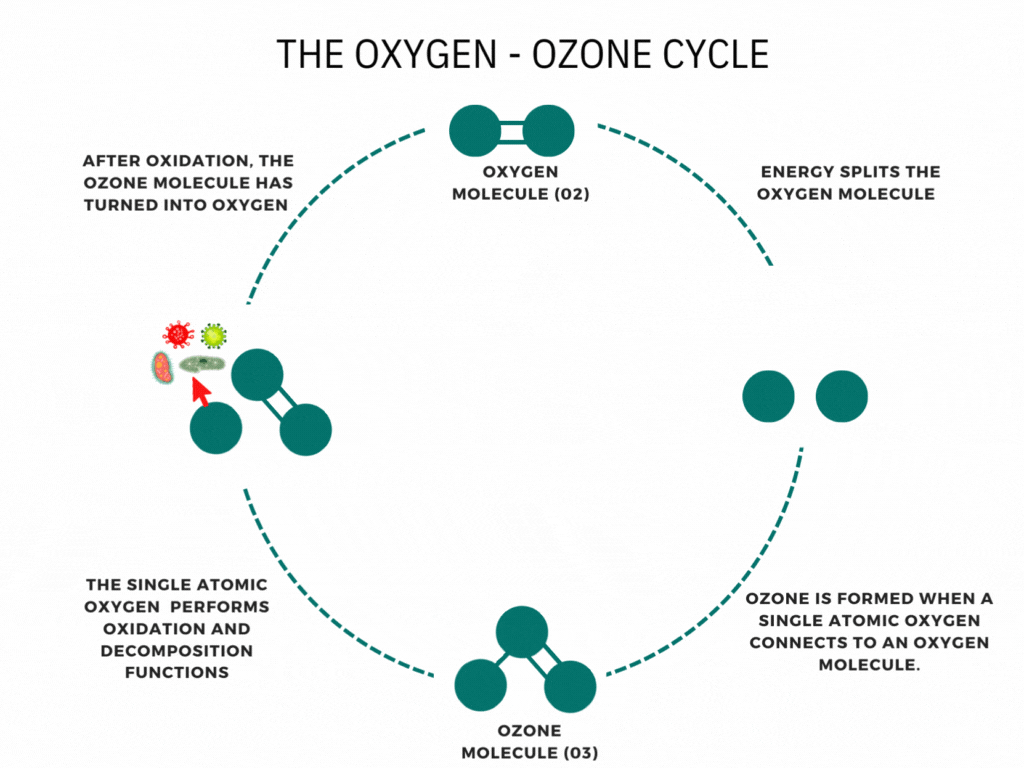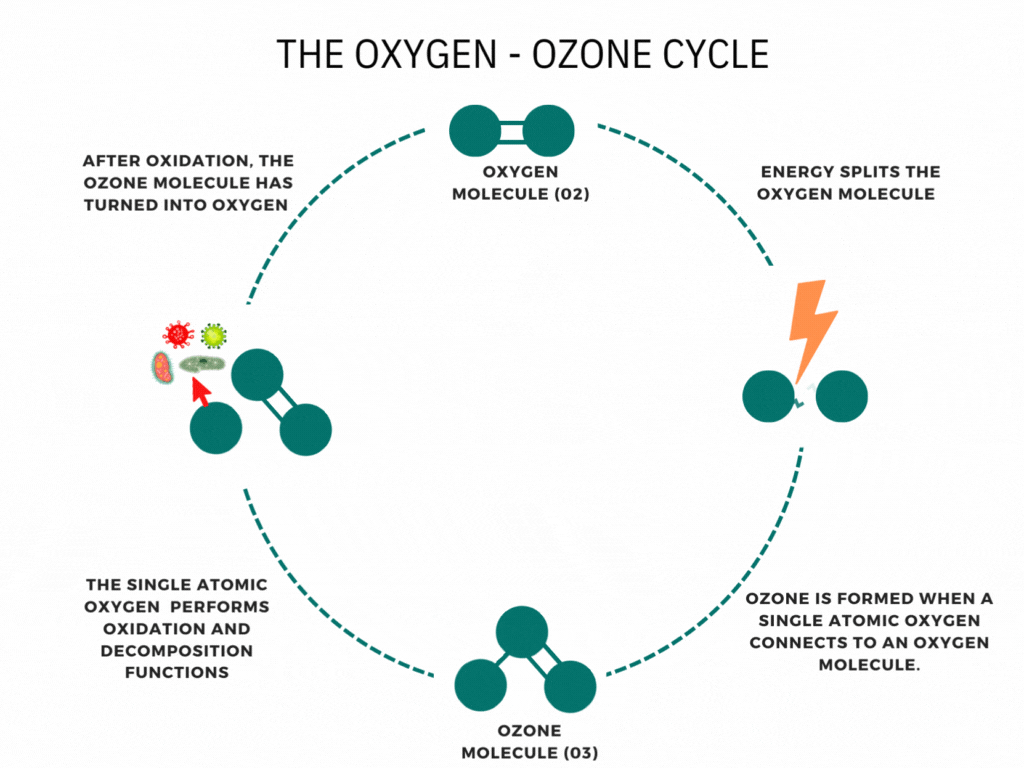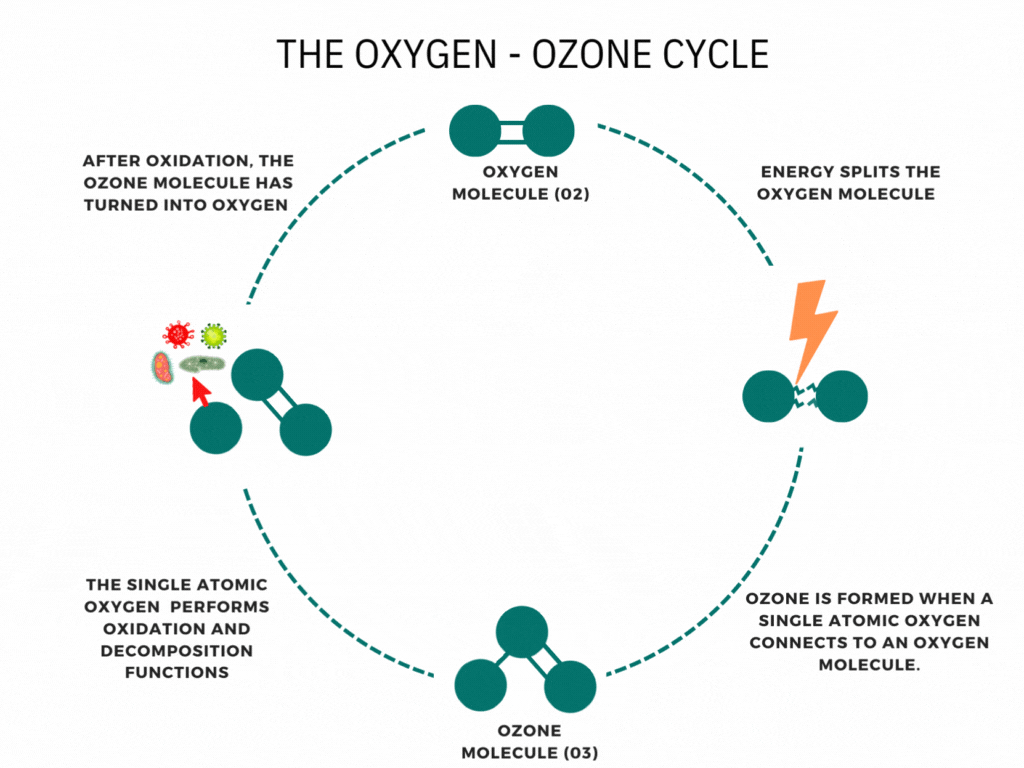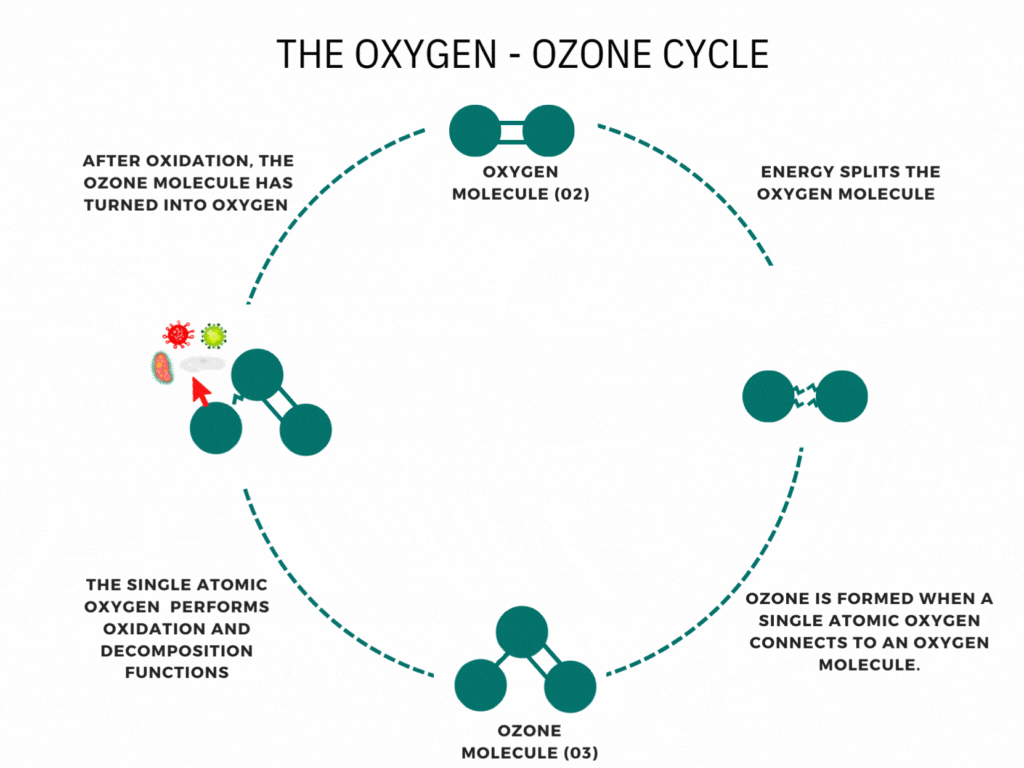
Ozone is a molecule that forms when an oxygen molecule receives an extra oxygen atom. It occurs naturally through some chemical reactions, such as the creation of the ozone layer by the sun’s UV rays, and can also be produced during thunderstorms and waterfalls. While these examples are commonly associated with ozone, it is less well-known that it can also be artificially produced for disinfection. Ozone generators use high voltages or UV light to create ozone artificially by decomposing oxygen molecules into individual oxygen atoms. These radicals can then combine with oxygen molecules to form ozone (O3). The ozone molecule is unstable, has a short lifespan, and cannot be stored or transported, necessitating on-site production. Ozone generators intentionally produce ozone gas, emitting high levels of ozone.
How Ozone Generators Work
Ozone generators harness electrical energy to split oxygen molecules (O2) into individual oxygen atoms. These individual oxygen atoms combine with other oxygen molecules to form ozone (O3). This fascinating process, known as ozone generation, is the cornerstone of ozone generators’ function. Using methods such as corona discharge, these devices produce ozone gas, a powerful oxidizing agent. This ozone gas can be utilized for various applications, including water treatment, air purification, and industrial processes. Understanding how ozone generators work helps us appreciate their role in improving air and water quality and supporting industrial operations.
How Does An Industrial Ozone Generator Work?
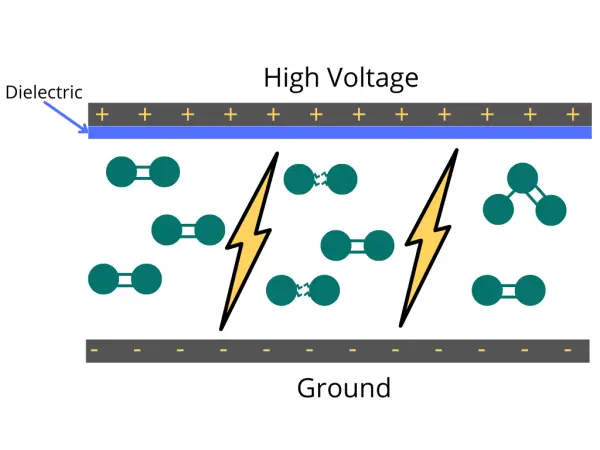
Have you ever been curious about how ozone generators work? Ozone generation operates on the principle of Corona discharge. It replicates lightning strikes in a controlled environment. This principle has different names depending on the type and style of the generator (dielectric barrier discharge, corona discharge, plasma block, silent corona, etc.), but is fundamentally the same. It involves a diffuse electrical discharge through a dielectric material. The electric charge applied to the electrodes causes some oxygen molecules to split apart and temporarily combine with other oxygen molecules, forming a molecule of three oxygen atoms (O3). Ozone molecules are highly reactive due to their three oxygen atoms, enabling them to react with various contaminants in both air and water.
Ozone generators are essential in various industrial applications, offering an affordable and effective solution for oxidation. This powerful oxidant can destroy bacteria, viruses and other harmful pollutants. Ozone generators are a perfect solution if you require an industrial ozone generator for water treatment, a commercial ozone generator for air purification, indoor air pollution control, or an advanced oxidation system.
Ozone Generation Methods
There are two primary methods for generating ozone: corona discharge and ultraviolet (UV) light. Corona discharge involves using high-voltage electrical energy to split oxygen molecules into individual oxygen atoms. These individual oxygen atoms then combine with other oxygen molecules to form ozone. This method is highly efficient and capable of producing higher ozone concentrations, making it a popular choice for industrial applications.
On the other hand, UV light uses ultraviolet radiation to achieve the same result. The UV light splits oxygen molecules into individual oxygen atoms, which combine with other oxygen molecules to form ozone. While effective, UV light is generally less efficient than corona discharge and produces lower ozone concentrations. Both methods, however, are valuable for producing ozone for various applications, from air purification to water treatment.
Production and Concentration
Ozone generation refers to the amount of ozone produced over time, measured in grams per hour. Ozone concentration is the quantity of ozone in volume, measured in grams per cubic meter or percentage by weight. Understanding this concept is crucial before purchasing an ozone generator.
Industrial Ozone Generators vs. Air Cleaners
Industrial ozone generators are robust devices engineered for large-scale applications in various industries, producing substantial amounts of ozone for water treatment, semiconductors, remediation, and odour control. In contrast, air cleaner ozone generators, marketed for residential or commercial use, have lower ozone output, compact designs, and focus on removing some smell in homes or offices. While these devices claim to eliminate airborne particles and odours, users must exercise caution, as excessive ozone exposure can pose health risks. Elevated indoor ozone levels can be harmful when inhaled, especially for vulnerable groups like children and older people. Regulatory guidelines from agencies such as the EPA and NIOSH set standards for outdoor and indoor ozone levels to protect public health. Understanding the distinctions between these industrial and air-cleaner ozone generators is crucial for making informed decisions based on specific needs and usage scenarios.
The primary distinction between industrial ozone generators and air purifier ozone generators lies in the concentration of ozone they produce. Industrial generators are engineered to generate significantly higher ozone levels and are suitable for large-scale applications such as water treatment and odour control in industrial environments. These devices can reach concentrations that meet the specific requirements of industrial processes. In contrast, ozone generators designed for air purification in residential or commercial settings have considerably lower ozone output.
Applications of Ozone Generators
Ozone generators are incredibly versatile devices with a wide range of applications:
- Water Treatment: Ozone generators disinfect and purify water by removing bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. This makes them essential in ensuring safe drinking water and treating wastewater.
- Air Purification: These devices remove pollutants and contaminants, significantly improving indoor air quality and controlling indoor air pollution. They are instrumental in environments where maintaining clean air is crucial.
- Industrial Processes: Ozone generators play a vital role in various industrial processes, such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and textile manufacturing. Their ability to produce high ozone concentrations makes them ideal for these demanding applications.
- Medical Applications: Ozone generators are used in the medical field for wound treatment and the disinfection of medical equipment. Their powerful oxidizing properties help eliminate harmful pathogens and promote healing.
- Food Processing: Ozone generators also disinfect and preserve food products. They help extend the shelf life of food and ensure its safety for consumption.
Overall, ozone generators are indispensable tools that enhance air and water quality and support many industrial and medical processes. Their ability to control indoor air pollution and purify water makes them valuable assets in various settings.
How to size an ozone Generator
When selecting and sizing an ozone generator for a particular application, there are three crucial considerations to ensure effective results:
- Ozone Demand: The ozone demand is the most critical information when choosing an ozone generator for a project or application. It indicates how much ozone per volume of water or air is required to address an existing issue, typically the inactivation of bacteria or harmful contaminants. You can determine ozone demand through various means, including published scientific studies, CT (concentration-time) factor tables for bacterial deactivation, pilot testing, or governmental regulations.
- Volume: The volume of water, air, gas, etc., that requires treatment (m3/h, GPM, SLPM, etc.).
- Compensation: Proper compensation is crucial to account for factors limiting ozone’s involvement in the reaction. This compensation considers the efficiency of the ozone dissolution process, ozone concentration, and the ozone decomposition half-life. Once you determine the ozone demand, multiplying it by the volume of gas, water, etc., that needs treatment provides a theoretical amount of ozone required for your project in an ideal situation.
Implementing adequate compensation for all contributing factors limiting ozone participation in reaction factors over ozone production will prevent under-sizing the ozone system and achieve better treatment results. For all industrial applications, it’s essential to note that ozone generators designed for air purification cannot effectively address the complexities of industrial challenges. While air purifier ozone generators may suffice for smaller-scale residential or commercial needs, the demands of industrial processes, such as large-volume water treatment or robust air purification in expansive spaces, often exceed their capabilities. Industrial ozone generators are specifically engineered to deliver the required ozone concentrations and volumes, ensuring successful remediation of issues like bacterial inactivation or pollutant removal. Therefore, selecting an ozone generator tailored to the specific demands of the industrial application is paramount for achieving optimal and reliable results.